Planting Zone Map – Backstory
There are a few steps that we need to perform to complete a task. Without performing those steps, it will be difficult to start a task, let alone complete it. Beginners and rookies in every field make some errors that result in financial loss. It is fine to make these mistakes, but when the final result has a big impact, it is better to have information beforehand.
The same mistakes are common in the field of agriculture. Take your time with this decision if you are a new farmer and want to plant any crop. If you want to keep up with the news, an interesting piece came out a few months ago on our screens. We found out recently that the USA Planting zone map has been updated. For a new farmer, this news is important for their future. All plant lovers need to understand the plant zone map to get the best crop based on their hard work.
Planting Zone Map – Introduction
Before proceeding to the plantation process, a new farmer needs to learn some factors related to planting. One of those points is the Planting zone map. This map is also known as the hardiness zone map. This map is a vital tool for farmers and gardeners. The map helps farmers understand the ideal location to plant a seed based on the climate and temperature.
This map is essential for farmers to understand different factors that relate to planting. The factors depending on the map are landscaping, gardening, and plantation. Also, the map helps you make different decisions that positively impact your plant’s health and life.
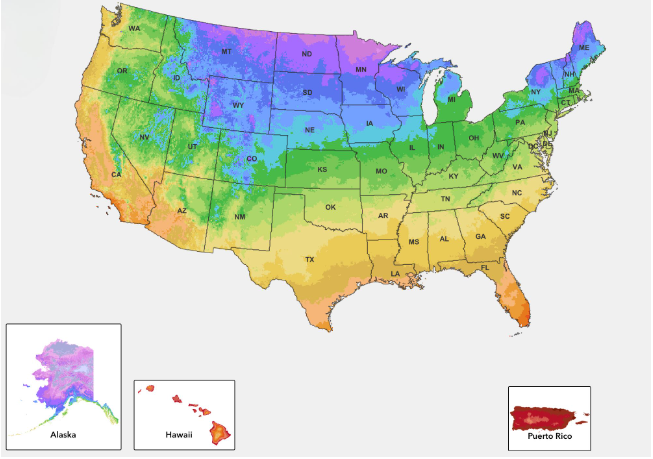
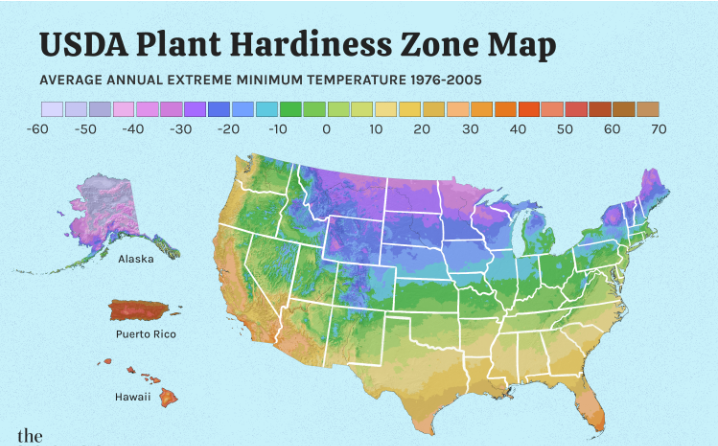
A planting zone map is available according to the color code and also according to the annual average extreme minimum temperature in an area. It is better to have an internet connection while using this map. A garden zone map also offers the option to enter the zip code to search for details regarding farming in your area.
planting zone map
Planting Zone Map – How to read the map
Now that we understand the meaning of this map for farmers, it is vital to know its meaning. The map is divided into different zones based on the average minimum temperature. The zone map has ten temperature categories ranging from zone 1 to zone 13. Zone 1 on the map is the coldest, while zone 13 is the warmest zone for plantation. Also, each zone has two sub-zones marked as ‘a and b’. If you observe markings 7a and 7b, both zones refer to the cold and warm zones of Zone 7.
These markings in the map zone help us understand the extreme weather and temperature differences between the two regions of the US. Instead of writing the difference itself, these words are shorthand for communication between farmers and experts. The zone numbers are as per the perennial plans and their descriptions. Nurseries and plant suppliers share the details of perennial plants with the map experts.
On every map, you will find color-coded areas as well. These areas are per the chromatic spectrum we get by a prism. This way, we’ll get a graphical representation of different zones. If you observe two chromatic spectrums forming an overlay in a region, it helps the farmers to understand the cold hardiness. Further, the overlay of colors also helps the farmers compare different cold-hardiness for plants.
As per this information, the experienced select the correct plants per their region. Also, the information a farmer gets from the color overlay helps determine a plant’s performance in other regions of the country.
Using Planting Zone Map For Farming
Understanding the map from a general perspective is different from applying the information to your advantage. If you plan to plant crops on a larger scale, this map should be your guideline. You can use this map as the general guideline for perennial plants over the US. We should note that the perennial plant guideline is per the lowest average temperature but not the lowest ever temperature.
Average Temperature
Also, the map does not represent the coldest temperature ever but only shows the lowest average temperature. We need to be careful while planting a seed based on the average temperature data. Things can be different if your plants have thrived for years in a place, but you are trying to grow them in the coldest area. Since the zone map shows average temperature, your crop can face extreme cold for a year. Thus, the crop will be lost quickly, leaving you with disappointment and financial loss.
Use Info With Experience
Although the map is helpful for the farmers, the experienced farmers know that we can’t depend on the zone map for plantations in the future. Combine the info you get from the planting zone map with advice from local experts and farmers. Also, you can get help from the experts on the web. This rare combination will help you get the best results out of your efforts in farming.
Environmental Factors
Along with the hardiness zone, we can observe other environmental factors in this zone map. These factors are crucial in deciding the future of a plant. Some factors that affect a plant’s life are pollution, snow, sunshine, humidity, and moisture. Also, other factors that are vital for a plant are soil, wind, and soil type. Further, moisture balance and warm season heat are also things to consider while planting a crop. Along with this information, the way of planting a seed, its health, and size are also crucial.
Planting Zone Map – The Background and Uses
What should be your step if you are a regular follower of the zone map but see things getting a little different in the latest update? Does the different zone contradict the previous updates on the zone map? After checking the zone map, should you remove all the plants you have planted? These are the few questions every farmer will get upon reading about the planting zone map.
No matter the latest planting zone changes, it doesn’t mean you should forget all the previous editions. Your hard work will yield the best results contrary to the zone map. So, keep everything the same as your routine for the particular plant.
If you want to get the plants that are not ready for your zone, you should keep a point in mind about this map. The discussed map doesn’t share the lowest possible temperature in the past or future. But it only shares an average annual minimum temperature for 30 years. Thus, you can observe a lower temperature in the future as well.
We know different zones have the most detailed markings on this map. However, even after such details, there are climatic changes on the micro level that are not possible to add or display in this planting zone map. Therefore, small-town farmers should depend on their experience instead of broad-scale data.
Microclimate Details in The Zone Map
When we say microclimate, we mean that there are changes in temperature on the fine-scale level. These changes can be due to different reasons. If there is concrete or blacktop in a region, it can cause heat islands to form on a small scale. This difference is hard to mention on the zone map. Also, if an area has small hills or valleys, they can become the reason behind cold spots.
Microclimatic changes can occur in your garden as well. If you keep the garden covered during summer, its atmosphere will also be cooler than that of the neighboring areas. Thus, each garden can have a different climate. These changes can go in your garden as well. If you have an area in your garden near the southern wall, it will have a different zone map than other areas. Thus, the situation is possible if you observe climatic pockets in a smaller area.
Based on these microclimatic changes in a smaller area, the zone map experts can’t display everything on the map. Thus, all the experts advise the local farmers and gardeners to use the zone map wisely. You should combine the map data with your experience and future weather predictions to get the best results.
Perennial Plants and Hardiness
Now, as we understand the different details of the zone map, we move to another vital point concerning planting in various regions. If you are thinking about planting a perennial crop, it is important to understand the behavior of these plants. Some perennial plants adjust well to colder climates, especially when days are shorter and we experience cold temperatures.
However, as the weather begins to change with longer days, we get warmer temperatures. During this time of the year, some perennial plants lose their hardiness. It is also possible that a plant may feel injured early during the winter even though the temp won’t be at the lowest average. Also, if you live in an area where you observe sudden weather changes after the end of winter, the process may hurt your plant.
Thus, experienced farmers take plant zone information and apply it to the characteristics of their crops. This combination gets them the required results of their efforts and hard work.

planting zone map
Factors Affecting Plant Survival
The information that we collect from the hardiness zone map helps us with plantation and caring for our crops. However, other factors affect the survival of a plant. If we consider these factors, our data and info will be well-spent.
Light
It is an obvious point that light is the most important aspect of a plant’s survival. But every plant has a different requirement. New farmers sometimes expose the plant to extra Sunlight, causing brown leaves and dead plants. If your plant is at the limit of hardiness in your area, it needs partial light. The plant should be placed under a shelter where sunlight is available during the early hours of the day.
More info: Guide to Fast Growing Trees: Boost Your Landscape Quickly 2024
The situation can also go the other way for other plants. If your plant needs high sunlight during the winter, placing it near a colder area or under a shelter will also harm it.
Soil Moisture
This soil moisture is the point that most of the farmers neglect. Thus causing their crop to have worse effects despite all the initial efforts. Soil moisture is the most vital aspect of the health of a plant. But, each plant has a different need for soil moisture. Also, the requirement for soil moisture for a specific plant may vary every season. If a plant is hardly in your zone and gets treated with dry soil during autumn, the result may be damaging. Plants can also face moisture stress and give you a silent treatment due to moisture deficiency.
Temperature
The best temperature for a plant’s life is optimal. You can’t keep your plant in any of the extreme conditions. For most plant types, an average temp is the best. There is a range of suitable temperatures for each plant, and the temperature can change from season to season. But if you are a new farmer, keep the plants in a mixed environment. A place where they get Sunlight and little shelter will give you the best results.
Humidity
If your plant is experiencing a cold injury, the best remedy is to put it in a high-humidity region. This step will reduce moisture loss from the plant, reducing the effects of cold injury. If the area has low humidity, a cold injury may be adverse for the plants. Thus, in colder regions, the plant needs extra Sunlight and attention.